Why Choose a Diode Laser?
Compact and Efficient
What Is a Diode Laser?
A portable diode laser uses advanced DPSS technology, offering portability and precise engraving capabilities.
Why Buy a Diode Laser?
Diode lasers are perfect for compact workspaces and are great for marking metals, plastics, and ceramics. In the diode laser vs CO2 laser comparison, diode lasers often appeal to those who prioritize portability.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Compact Design | Fits any workspace |
| High Precision | Perfect for intricate detailing |
| Portable | Easy to move and set up |
| Energy Efficient | Low operating costs |
Recommended Product: Monport GQ 20W Diode Laser Engraver
- Best for: Jewelry engraving, detailed markings on small objects, and hobbyist projects
- Top Features: Lightweight design, FDA-approved safety, and fast setup
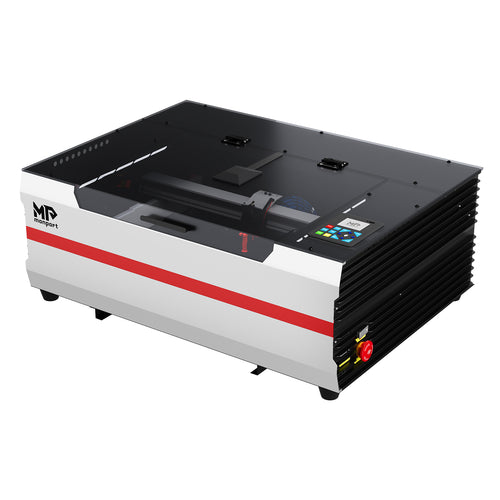
Why Choose a CO2 Laser?
Versatile and Powerful
What Is a CO2 Laser?
CO2 lasers excel in versatility, offering the ability to cut and engrave a wide range of materials with precision. Many users looking into diode laser vs CO2 laser options choose CO2 for its powerful cutting abilities.
Why Buy a CO2 Laser?
CO2 lasers are ideal for business owners, artisans, and creators who need a reliable machine for diverse applications.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Versatile Materials | Works with wood, acrylic, fabric, and more |
| High Beam Quality | Ensures precision and clean edges |
| Durable Build | Built to last for long-term use |

Monport 40W Lightburn-ready (12" X 8") CO2 Laser Engraver & Cutter with FDA Approval - 40W Basic
Recommended Product: Monport 40W CO2 Laser Engraver & Cutter
- Best for: Cutting and engraving larger materials like wood, acrylic, and leather
- Top Features: LightBurn compatibility, large workspace, and professional-grade results
Compare Diode and CO2 Lasers
| Feature | Diode Laser | CO2 Laser |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Compact and portable | Larger and more robust |
| Material Capability | Ideal for thin materials and metals | Versatile for thick and thin materials |
| Precision | Excellent for fine details | Superior for large-scale precision |
| Applications | Jewelry, small engravings | Woodworking, acrylic cutting |
FAQs
Takeaways
- Diode Lasers: Compact, portable, and perfect for engraving metals and detailed designs.

- CO2 Lasers: Versatile, high-quality, and suitable for cutting and engraving on diverse materials.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between a portable laser engraver and a CO2 laser depends on the intended application, budget, and specific requirements. Portable laser engravers are more suitable for compact and portable systems, with fast processing speeds and precision engraving capabilities. On the other hand, CO2 lasers offer versatility and higher beam quality, making them ideal for cutting and engraving various materials. Consider the pros, cons, applications, and FAQs provided above to make an informed decision on which laser type is best for your needs in the diode laser vs co2 laser comparison or when looking for an engraving machine for sale.
Unlock Big Savings at Monport Laser! Use code BESTMP10 at checkout for an exclusive discount – Click here to shop now!
Read More: Diode Lasers Vs Monport K40 Lightburn Lasers